The 7 Core Pillars of Operational Excellence: Your Complete Guide
Operational excellence represents the systematic pursuit of flawless execution across all business functions.
It’s not merely about reducing errors or cutting costs—it’s a holistic approach that transforms how organizations deliver value to customers while maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
Transform your organization’s performance with proven improvement strategies
Learn the systematic approach to driving sustainable business success with Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification.

The foundation of true operational excellence lies in understanding and implementing its core pillars—the fundamental elements that support lasting transformation.
These pillars don’t exist in isolation but work together as an integrated system, much like the principles found in Six Sigma certification methodologies.
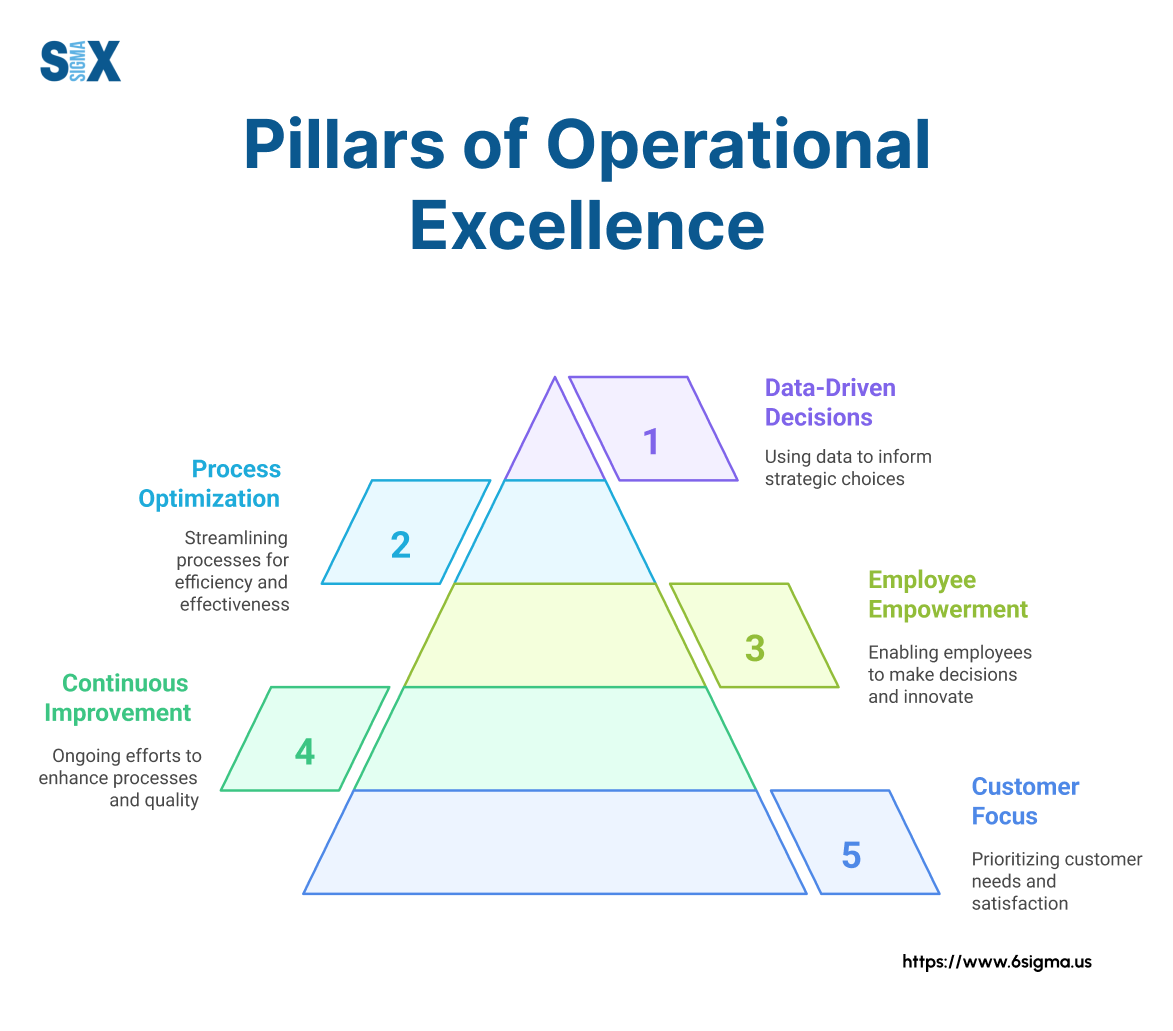
Key Highlights
- Strategic frameworks for sustainable improvement
- Process optimization techniques that work
- Customer-centric value creation approaches
- People development strategies for excellence
- Performance measurement systems that drive results
- Methods to build improvement cultures
- Technology integration for operational advantage
What Is Operational Excellence?
Operational excellence goes beyond simple efficiency improvements or cost-cutting initiatives.
It represents a philosophy where every aspect of an organization works in harmony to deliver maximum value to customers while minimizing waste and variation in processes.
Definition and evolution
At its simplest, operational excellence means consistently executing your business strategy better than competitors.
It requires organizations to develop systems that promote problem-solving at all levels, standardize best practices, and create a culture where improvement becomes habitual rather than exceptional.
The concept has evolved significantly over decades. What began as quality control in manufacturing has expanded into a multidimensional approach applicable across industries and functions.
Today’s operational excellence encompasses everything from strategic alignment and leadership practices to frontline execution and technological enablement.
Role in business success
For organizations implementing Lean principles, operational excellence represents the practical application of concepts like value stream mapping, pull systems, and visual management.
It transforms abstract principles into tangible business results through systematic implementation.
The core pillars of operational excellence provide the structure through which organizations can implement and sustain improvement efforts.
Rather than focusing on isolated initiatives, these pillars create an integrated system where improvements in one area naturally strengthen others.
Organizations that master operational excellence share common characteristics: they maintain unwavering focus on customer needs, they empower employees at all levels to identify and solve problems, they use data to drive decisions rather than opinions, and they view improvement as a continuous journey rather than a destination.
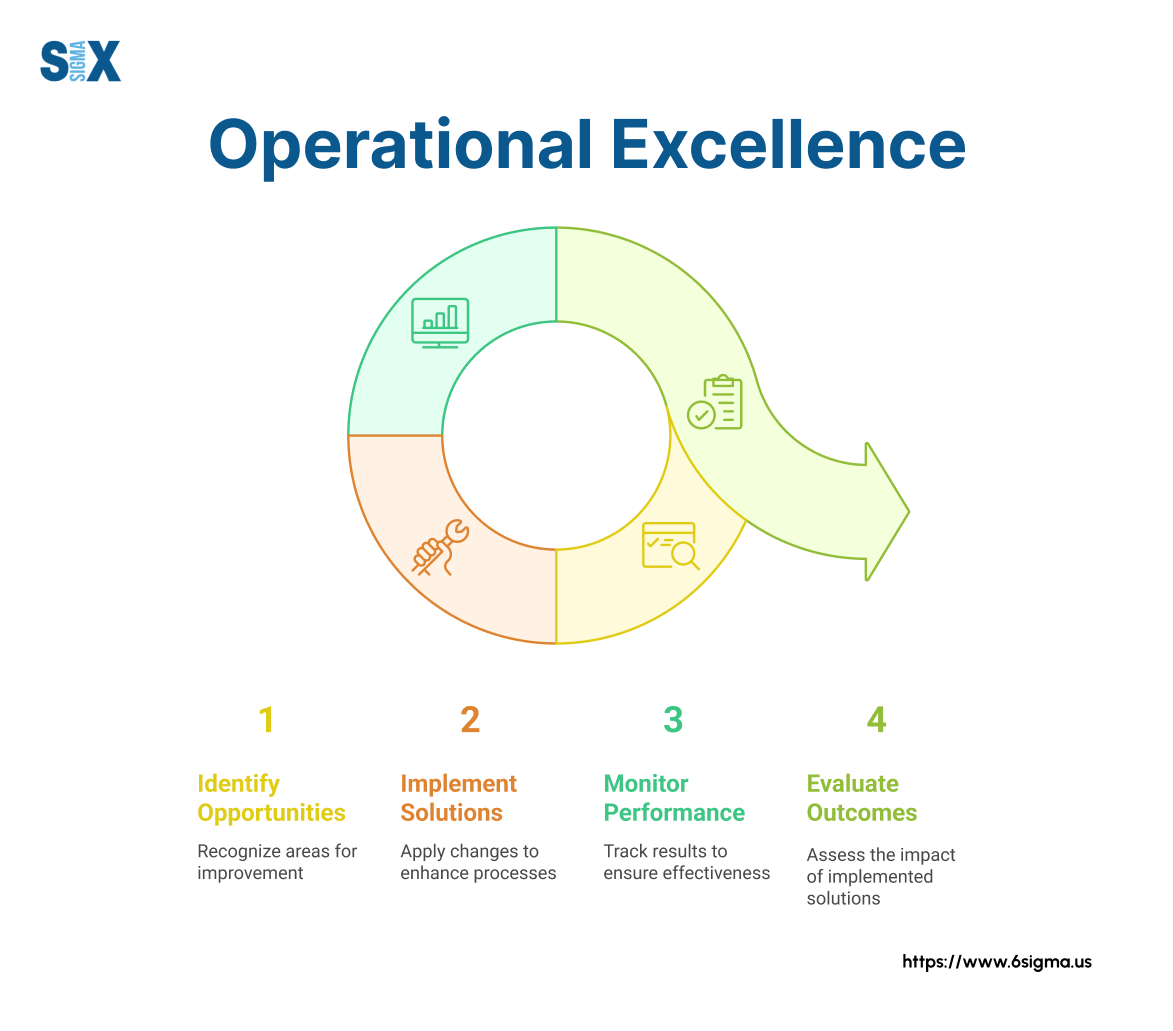
The Seven Core Pillars of Operational Excellence
The journey toward operational excellence requires a structured approach built on proven principles.
These seven core pillars of operational excellence provide the foundation for transforming organizational performance across industries and functions.
Pillar 1 – Strategic Leadership and Vision
Effective operational excellence begins with leadership commitment and clear strategic direction. Leaders must not only articulate a compelling vision for operational excellence but also demonstrate personal commitment through their actions and decisions.
Strategic leadership for operational excellence requires:
- Clearly defined organizational purpose and values
- Alignment between improvement efforts and business strategy
- Resource allocation that prioritizes long-term capability building
- Governance structures that track and accelerate improvement
- Communication systems that create shared understanding
Leaders play a crucial role in breaking down functional silos that often impede improvement efforts.
They must foster cross-functional collaboration and ensure that improvement initiatives receive appropriate resources and attention despite competing priorities.
The most effective leaders establish mechanisms that connect strategic objectives to daily operations. They create cascading goals and metrics that help employees understand how their work contributes to larger organizational priorities.
This connection between strategy and execution proves essential for sustained excellence.
Organizations pursuing Six Sigma certification programs find that leadership engagement determines program success. When leaders actively sponsor projects, remove barriers, and recognize achievements, improvement initiatives gain momentum and deliver lasting results.
Change management capabilities represent another critical leadership responsibility. Operational excellence initiatives often require significant changes to established processes and practices. Leaders must help their organizations navigate these transitions by addressing resistance, building coalition support, and celebrating early wins.
The most successful organizations develop leadership pipelines that emphasize operational excellence capabilities.
They select and promote leaders who demonstrate commitment to continuous improvement principles and who can balance short-term performance with long-term capability building.
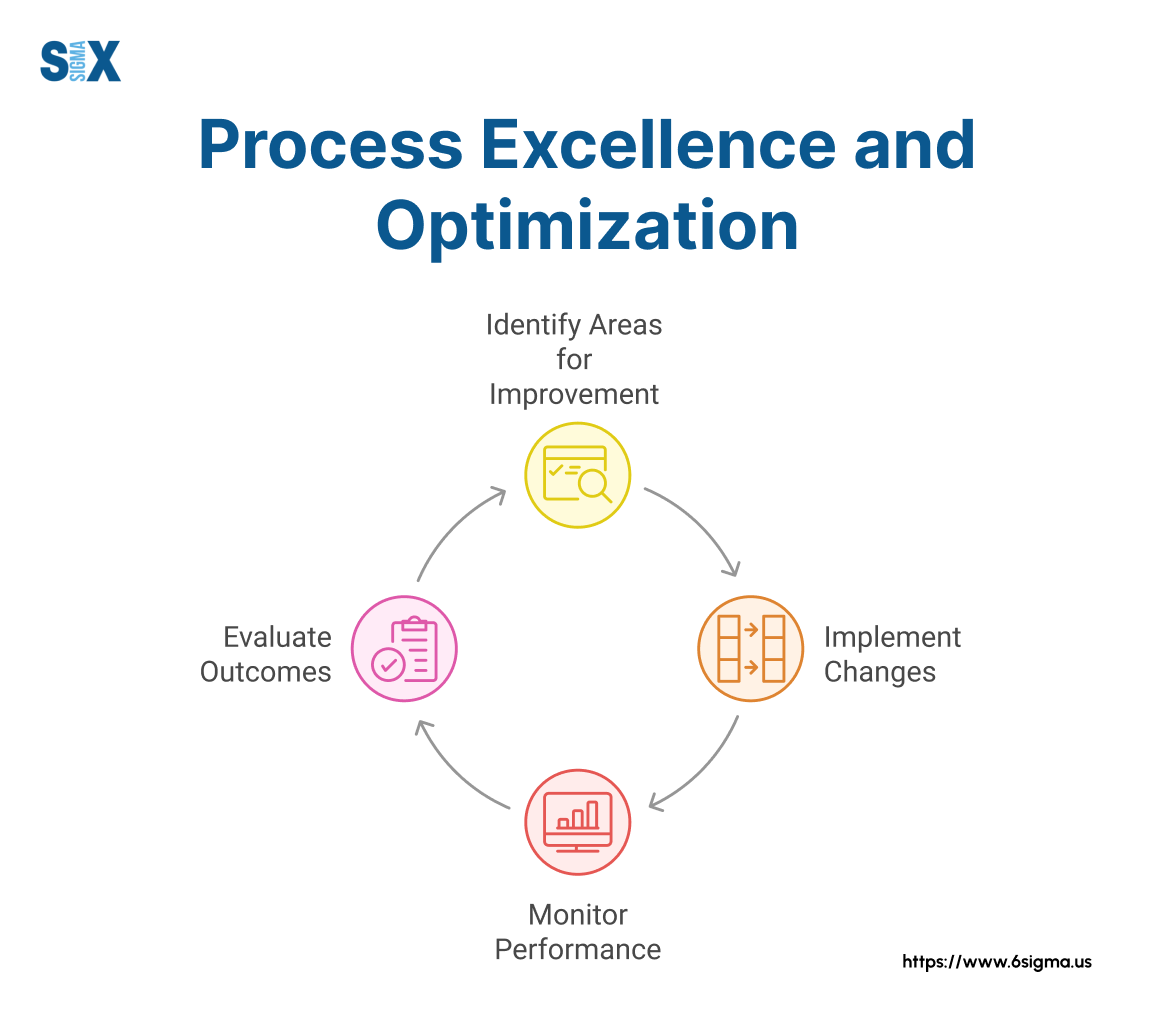
Pillar 2 – Process Excellence and Optimization
Process excellence forms the technical core of operational excellence.
It involves systematically designing, analyzing, and improving the workflows that deliver value to customers while eliminating waste, reducing variation, and increasing reliability.
Effective process excellence requires organizations to:
- Map and understand current processes
- Identify value-adding and non-value-adding activities
- Standardize best practices while allowing appropriate flexibility
- Reduce complexity that creates opportunities for errors
- Establish clear process ownership and accountability
Process mapping serves as a fundamental tool for improvement. By visualizing workflows, organizations can identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and disconnects that impede performance.
These visual representations create shared understanding and highlight improvement opportunities.
Root cause analysis represents another essential element of process excellence. Rather than addressing symptoms, organizations must develop capabilities to identify and address underlying causes of problems.
Techniques like the 5 Whys, fishbone diagrams, and statistical analysis help teams move beyond superficial understanding.
Waste elimination remains central to process excellence.
Organizations must systematically identify and eliminate the eight forms of waste: defects, overproduction, waiting, non-utilized talent, transportation, inventory, motion, and extra processing. This focus on waste reduction improves both efficiency and effectiveness.
Quality management systems provide the structure through which process excellence initiatives operate.
These systems establish standards, measurement approaches, and improvement methodologies that ensure consistent execution and continuous enhancement of key processes.
Organizations that excel at process optimization develop capabilities to analyze process performance quantitatively.
They use statistical tools to understand process capability, identify variation sources, and verify improvement impacts.
This data-driven approach eliminates guesswork and focuses efforts where they’ll deliver maximum value.
Unlock advanced techniques to diagnose and eliminate organizational inefficiencies
Develop statistical skills that transform complex business challenges with Six Sigma Black Belt.
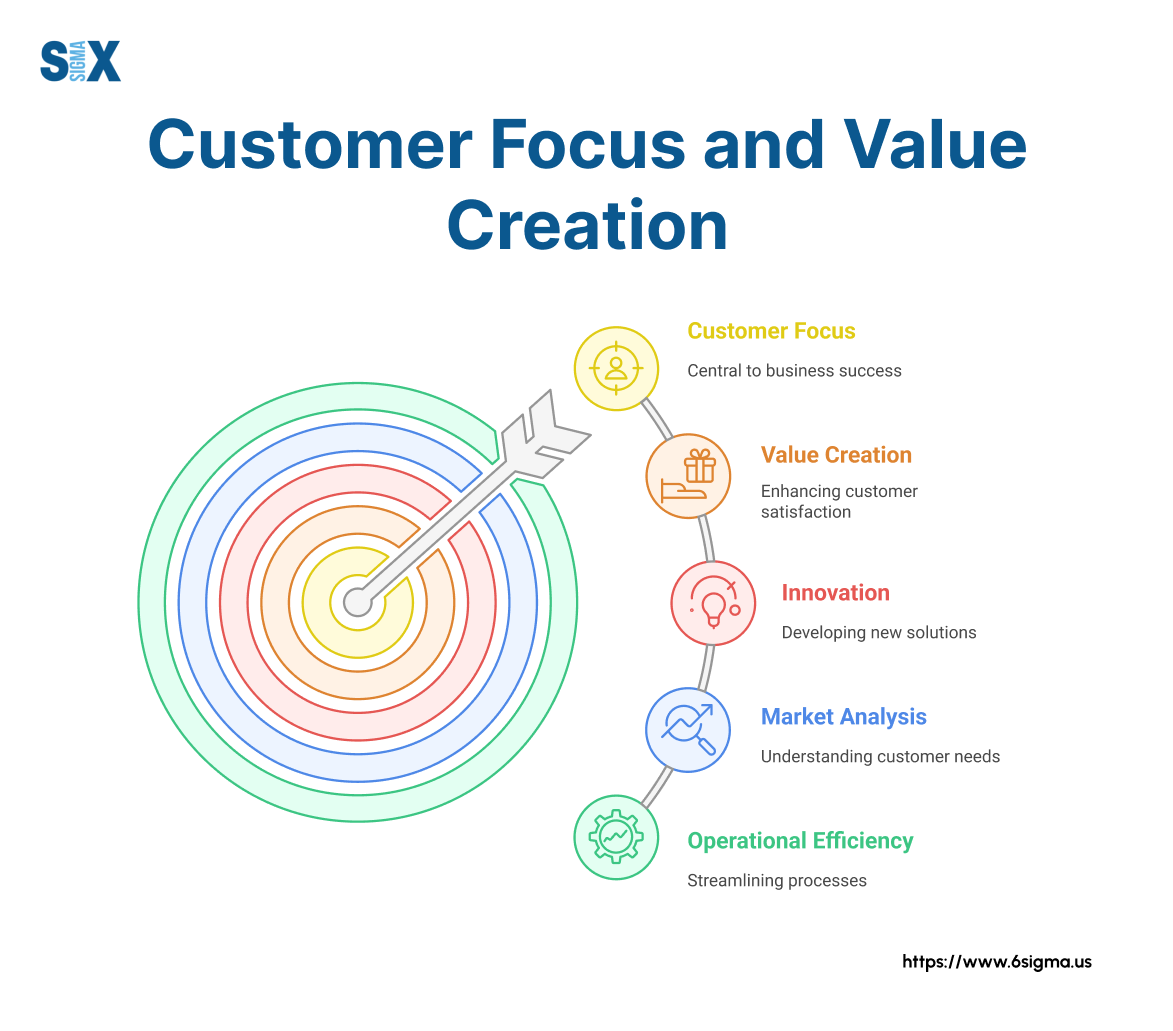
Pillar 3 – Customer Focus and Value Creation
Operational excellence must ultimately serve customer needs.
Organizations that excel in this pillar develop deep understanding of customer requirements and systematically translate those insights into products, services, and experiences that deliver exceptional value.
Effective customer focus requires:
- Systematic methods for capturing customer needs and expectations
- Processes for translating customer requirements into specifications
- Value stream mapping to optimize end-to-end customer journeys
- Regular measurement of customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Mechanisms for rapidly addressing customer concerns
Voice of customer (VOC) programs provide structured approaches for gathering customer insights. These programs use surveys, interviews, observation, and data analysis to identify stated and unstated customer needs.
Organizations then translate these insights into specific, measurable requirements that guide improvement efforts.
Value stream mapping represents a powerful tool for optimizing customer journeys.
By mapping the entire process from initial customer contact through delivery and follow-up, organizations can identify and eliminate steps that don’t add value from the customer’s perspective.
Organizations implementing Lean fundamentals recognize that value must be defined from the customer’s perspective.
This customer-centric definition of value guides decisions about which activities to enhance, which to eliminate, and which to redesign completely.
Customer journey optimization extends beyond traditional process improvement by considering emotional and experiential aspects of customer interactions.
Organizations map key touchpoints and develop strategies to enhance moments that matter most to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The most customer-focused organizations develop closed-loop systems that connect customer feedback directly to improvement initiatives.
They establish clear accountability for addressing customer concerns and create metrics that track resolution effectiveness and speed.
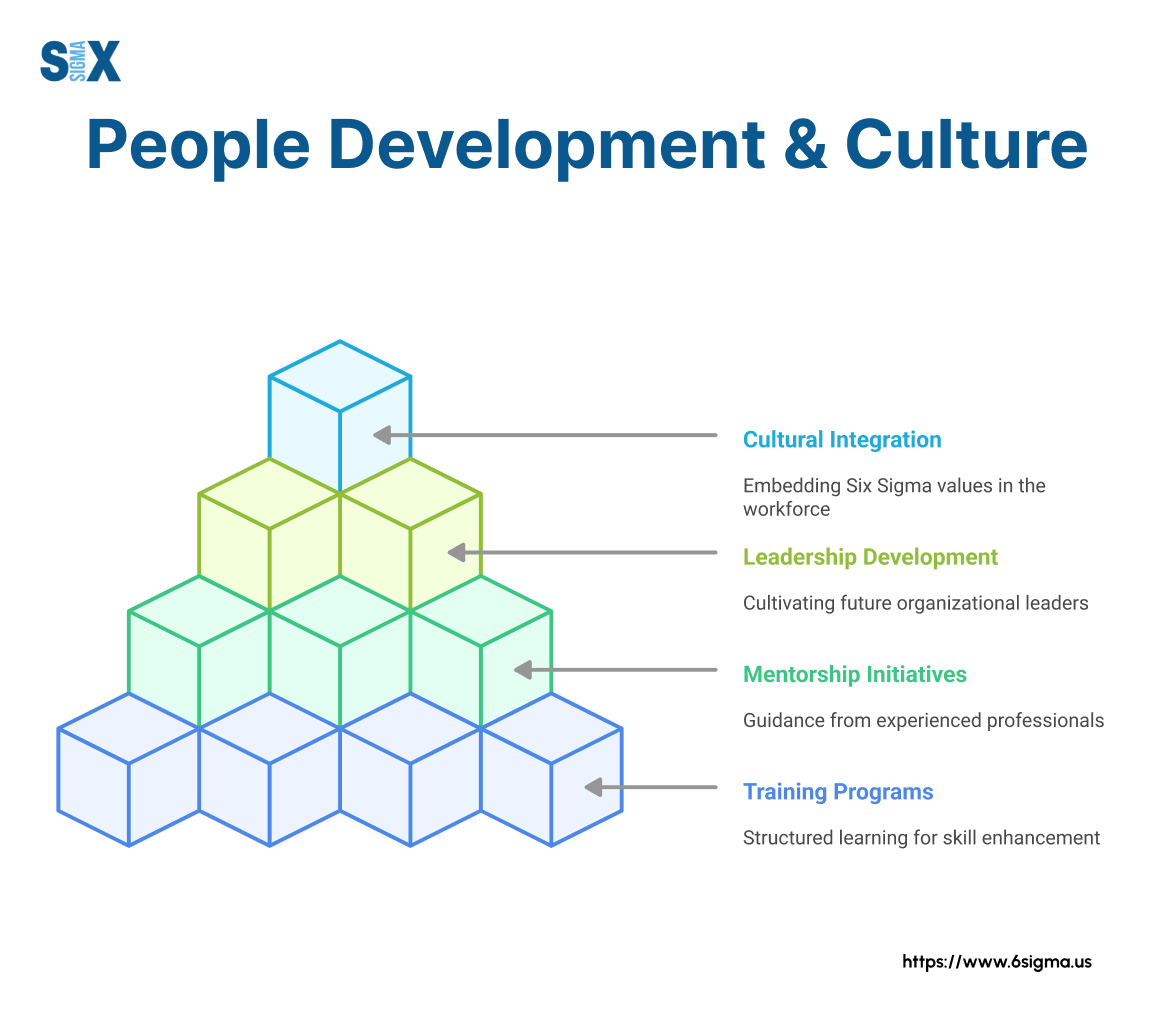
Pillar 4 – People Development and Culture
People ultimately drive operational excellence. Organizations must develop workforce capabilities, engagement, and cultural attributes that support continuous improvement and operational discipline.
Effective people development strategies include:
- Comprehensive training programs aligned with business needs
- Career paths that recognize and reward improvement capabilities
- Engagement approaches that tap employee creativity
- Team structures that promote collaboration and knowledge sharing
- Recognition systems that reinforce desired behaviors
Training represents a foundational element of people development. Organizations pursuing operational excellence create structured learning paths that build capabilities at all levels.
For many, this includes formal certification programs like Green Belt and Black Belt that develop technical and leadership skills.
Cultural transformation often proves the most challenging aspect of operational excellence.
Organizations must shift from blame-oriented cultures to problem-solving cultures where issues are viewed as improvement opportunities rather than failures to be hidden or punished.
Employee engagement drives sustainable improvement. Organizations that excel in this pillar create mechanisms for employees to contribute ideas, participate in improvement projects, and take ownership of their work processes.
This engagement taps the creativity and knowledge of those closest to the work.
Team structures play important roles in operational excellence.
Cross-functional teams break down silos that impede improvement, while specialized improvement teams provide technical expertise and project management capabilities for complex initiatives.
Leadership development deserves special attention.
Organizations must develop leaders who understand improvement methodologies, can coach others effectively, and model the behaviors required for operational excellence.
This leadership pipeline ensures sustainability as the organization evolves.
Develop leadership capabilities that drive organizational change
Learn to create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation with Six Sigma Champion – Leadership Program.
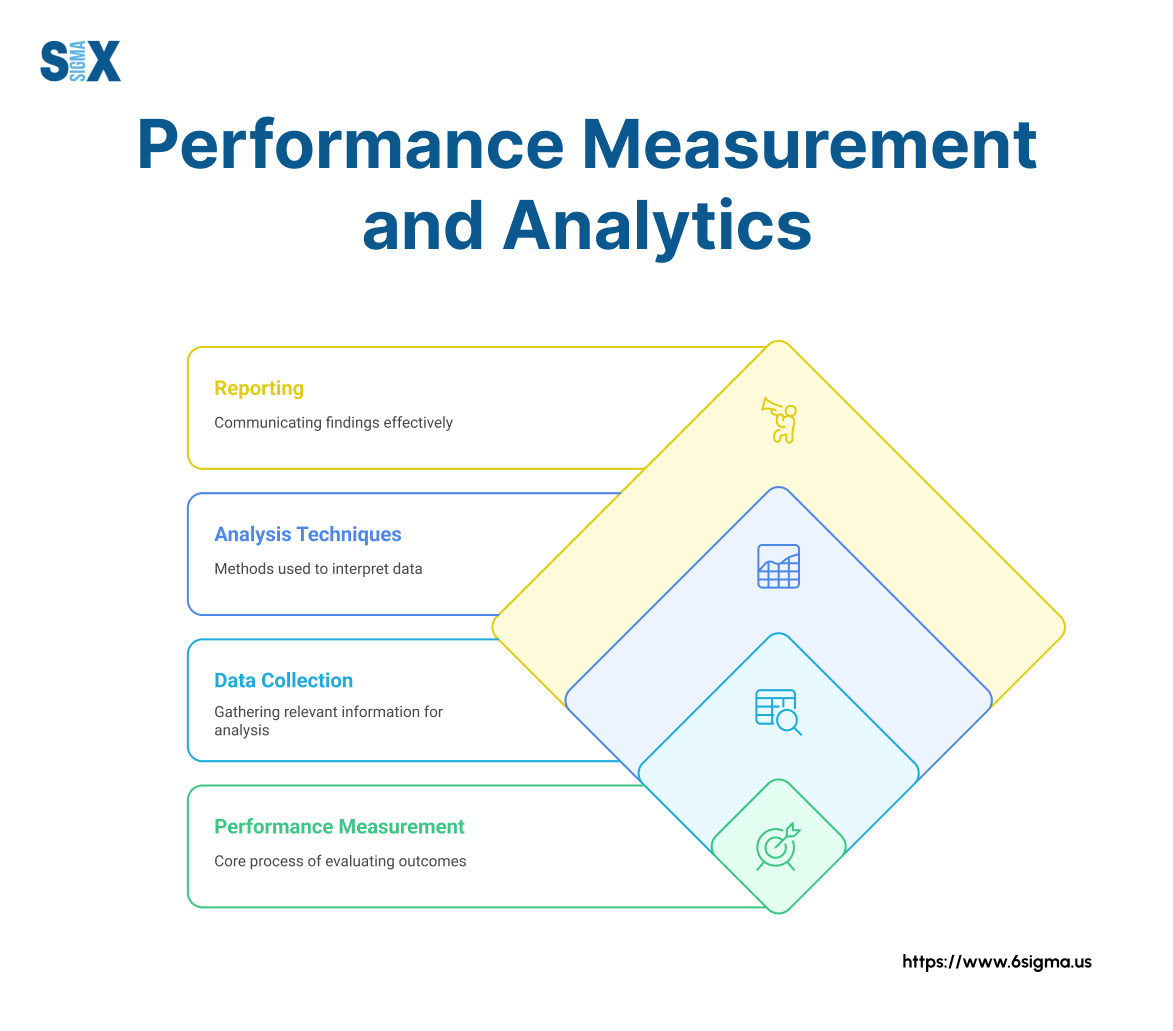
Pillar 5 – Performance Measurement and Analytics
What gets measured gets managed. Organizations pursuing operational excellence develop sophisticated measurement systems that track performance, identify improvement opportunities, and verify the impact of initiatives.
Effective performance measurement includes:
- Balanced scorecard approaches that address multiple dimensions
- Leading and lagging indicators that provide complete perspective
- Visual management systems that create transparency
- Statistical process control methods that distinguish signals from noise
- Data governance practices that ensure information quality
Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide the metrics through which organizations track operational excellence progress. Effective KPI systems balance financial measures with operational, customer, and people metrics to prevent suboptimization and ensure holistic improvement.
Data-driven decision making represents a core capability for operational excellence.
Organizations must develop the discipline to base decisions on facts rather than opinions, using appropriate analytical tools to understand problems and evaluate potential solutions.
Statistical process control methods help organizations distinguish between normal variation and special causes requiring intervention.
These techniques prevent overreaction to random fluctuations while ensuring appropriate response to significant performance changes.
Master Black Belts often lead analytics capability development within organizations. They bring advanced statistical knowledge, coaching capabilities, and strategic perspective that help organizations extract maximum value from performance data.
Visual management systems make performance transparent and accessible.
Rather than hiding data in reports, organizations create visual displays that show current performance, targets, and improvement initiatives. These displays promote awareness, accountability, and action.
The most advanced organizations develop predictive analytics capabilities that identify potential issues before they impact performance.
These forward-looking approaches enable proactive intervention rather than reactive problem-solving.
Pillar 6 – Continuous Improvement Culture
Operational excellence requires more than occasional improvement projects. Organizations must develop cultures where improvement becomes part of everyday work rather than a separate activity.
Building continuous improvement cultures involves:
- Standardized improvement methodologies
- Regular improvement routines and cadences
- Recognition systems that reinforce improvement behaviors
- Knowledge management systems that capture and share learning
- Governance structures that sustain improvement focus
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle provides a fundamental structure for improvement activities.
Organizations embed this scientific approach to problem-solving throughout their operations, creating common language and methodology for addressing opportunities.
Kaizen principles emphasize that many small improvements often deliver greater impact than a few large initiatives.
Organizations create mechanisms for employees at all levels to identify and implement incremental improvements to their daily work.
Yellow Belt certification and training often serves as an entry point for building broad-based improvement capabilities. This foundational training helps employees understand basic improvement concepts and participate effectively in team initiatives.
Innovation management complements continuous improvement by creating pathways for more disruptive changes.
While continuous improvement optimizes existing processes, innovation introduces fundamentally new approaches that may deliver step-change performance improvements.
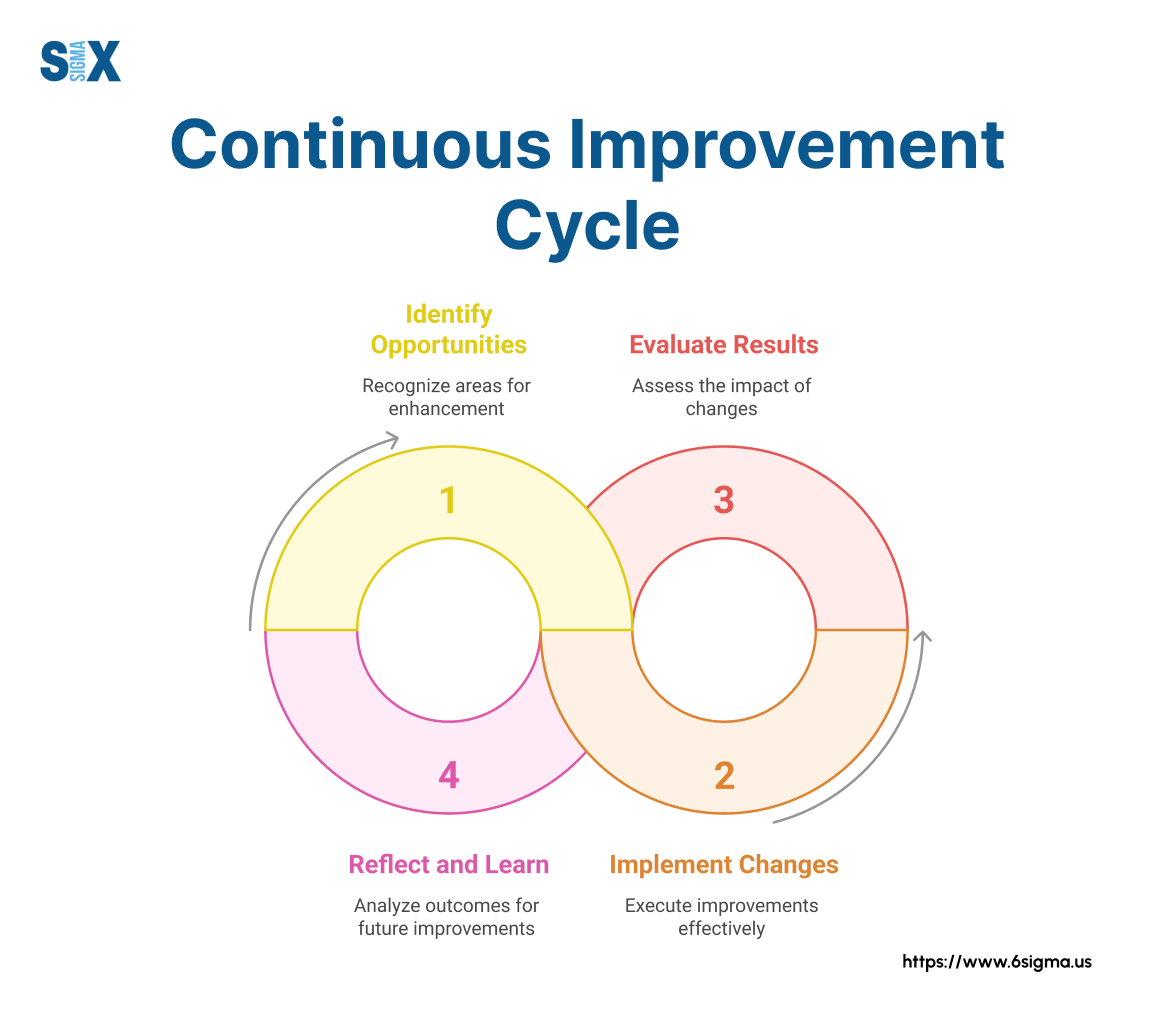
Pillar 7 – Technology and Digital Integration
Technology increasingly enables and accelerates operational excellence. Organizations must strategically leverage digital tools to enhance process performance, decision-making capabilities, and customer experiences.
Effective technology integration includes:
- Digital process automation opportunities
- Advanced analytics and visualization tools
- Collaboration platforms that connect dispersed teams
- Knowledge management systems that capture learning
- Integration architectures that connect disparate systems
Digital transformation extends beyond simply automating existing processes. Organizations must rethink how work gets done, leveraging technology to eliminate steps, enhance decision-making, and create new value propositions for customers.
Automation opportunities exist across most organizations. By identifying repetitive, rule-based activities, organizations can implement robotic process automation (RPA) and other technologies that improve speed, accuracy, and consistency while freeing human resources for higher-value work.
Data analytics platforms provide the infrastructure through which organizations collect, analyze, and leverage operational data.
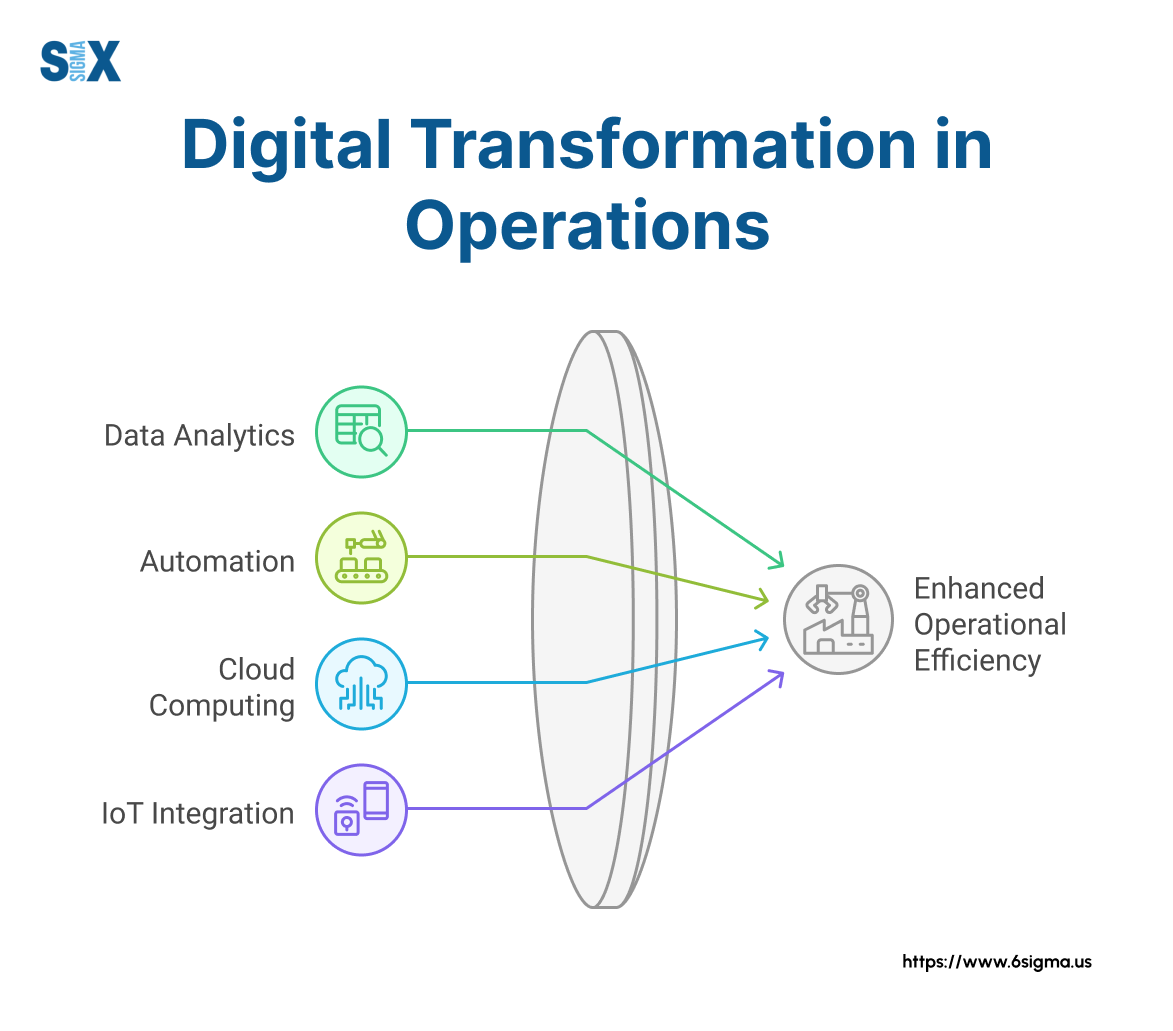
These platforms enable real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and simulation capabilities that enhance decision quality and speed.
White Belt fundamentals help organizations build broad awareness of improvement principles before implementing technology solutions.
This foundation ensures that technology serves strategic objectives rather than simply automating inefficient processes.
Curious about operational excellence but unsure where to start?
Prepare yourself for digital transformation and technological integration with Lean Six Sigma White Belt Certification.
Implementing The Pillars of Operational Excellence: A Practical Approach
Moving from theory to practice requires a structured approach to implementing the pillars of operational excellence.
Organizations that successfully embed these principles follow a methodical path that begins with honest assessment and proceeds through careful planning, execution, and reinforcement.
The assessment phase establishes your starting point. Before implementing changes, organizations must evaluate their current state across each pillar.
This assessment identifies strengths to leverage and gaps to address. Effective assessments combine quantitative metrics with qualitative insights from stakeholders at multiple levels.
Many organizations use maturity models that define progressive capability levels for each pillar, allowing teams to pinpoint their current position and set realistic improvement targets.
Implementation follows a roadmap that sequences initiatives for maximum impact. Rather than attempting to advance all pillars simultaneously, successful organizations prioritize based on business needs and organizational readiness.
The roadmap typically spans 18-36 months and includes specific milestones, resource requirements, and accountability assignments.
Early phases often focus on building foundational capabilities in leadership alignment and performance measurement before tackling more complex cultural and technological transformations.
Common implementation challenges include resource constraints, competing priorities, and resistance to change.
Organizations overcome these obstacles through several proven approaches. Dedicated improvement teams with protected time ensure progress despite daily operational demands.
Executive sponsors remove barriers and maintain focus when other initiatives threaten to divert attention.
Change management techniques address resistance by involving stakeholders early, communicating benefits clearly, and celebrating visible wins that demonstrate value.
Success metrics track both implementation progress and business impact. Leading indicators measure activity completion, capability development, and behavioral changes.
These provide early feedback on implementation effectiveness. Lagging indicators track operational and financial outcomes that validate the business case for operational excellence.
The most effective measurement systems connect these metrics in cause-effect relationships that demonstrate how pillar implementation drives business results.
Governance structures sustain implementation momentum. Regular review sessions at multiple organizational levels ensure accountability for progress.
These sessions follow standardized formats that focus on accomplishments, obstacles, and next steps.
The governance system also includes mechanisms for adapting the implementation approach based on lessons learned and changing business conditions.
Future Trends In Operational Excellence
The pillars of operational excellence continue to evolve as business conditions change and new technologies emerge.
Organizations that maintain competitive advantage through operational excellence stay ahead of several important trends reshaping implementation approaches.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning represent perhaps the most transformative forces in operational excellence.
These technologies enable predictive maintenance that prevents equipment failures before they occur. They power process mining tools that automatically discover inefficiencies in complex workflows.
They enhance quality systems through computer vision that detects defects invisible to human inspectors.
While these applications deliver immediate benefits, their greater impact comes from freeing human resources to focus on innovation and customer relationships rather than routine monitoring and analysis.
Sustainability considerations increasingly integrate with traditional operational excellence objectives.
Organizations recognize that waste elimination serves both efficiency and environmental goals. Carbon footprint reduction becomes a standard metric alongside cost and quality measures.
Supply chain optimization balances traditional factors like cost and lead time with environmental impact and social responsibility.
This integration creates opportunities to align operational excellence initiatives with corporate sustainability commitments, potentially accessing new funding sources and stakeholder support.
Digital twins—virtual replicas of physical assets and processes—enable more sophisticated simulation and optimization. Organizations use these models to test improvement ideas virtually before physical implementation, reducing risk and accelerating results.
As digital twin technology becomes more accessible, it will likely become a standard element in the performance measurement and process excellence pillars.

Conclusion
The seven core pillars of operational excellence provide a proven framework for organizations seeking sustainable performance improvement.
By systematically implementing strategic leadership, process excellence, customer focus, people development, performance measurement, continuous improvement culture, and technology integration, organizations create self-reinforcing systems that deliver lasting competitive advantage.
Successful implementation requires more than technical knowledge.
Organizations must balance structured methodology with cultural transformation, data-driven decision making with employee empowerment, and short-term wins with long-term capability building.
This balanced approach ensures that operational excellence becomes embedded in organizational DNA rather than existing as isolated improvement projects.
The journey toward operational excellence never truly ends. As business conditions evolve and new technologies emerge, organizations must continuously refine their approaches while maintaining focus on fundamental principles.
Those that master this balance achieve the agility to adapt to changing conditions while maintaining the discipline to execute consistently.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs






