The Ultimate Guide to Project Life Cycle: Mastering the 5 Phases for Project Success
A successful project always has a story, from inception to completion. This story is what we call a project life cycle!
The project life cycle is at the core of project management. It’s a standard framework that guides a project from ideation to completion and then closure.
This article will equip you to:
- The fundamental phases of the project life cycle and why they matter
- How to effectively navigate each phase to ensure project success
- Critical considerations and best practices I’ve developed over two decades
- Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
What is a Project Life Cycle?
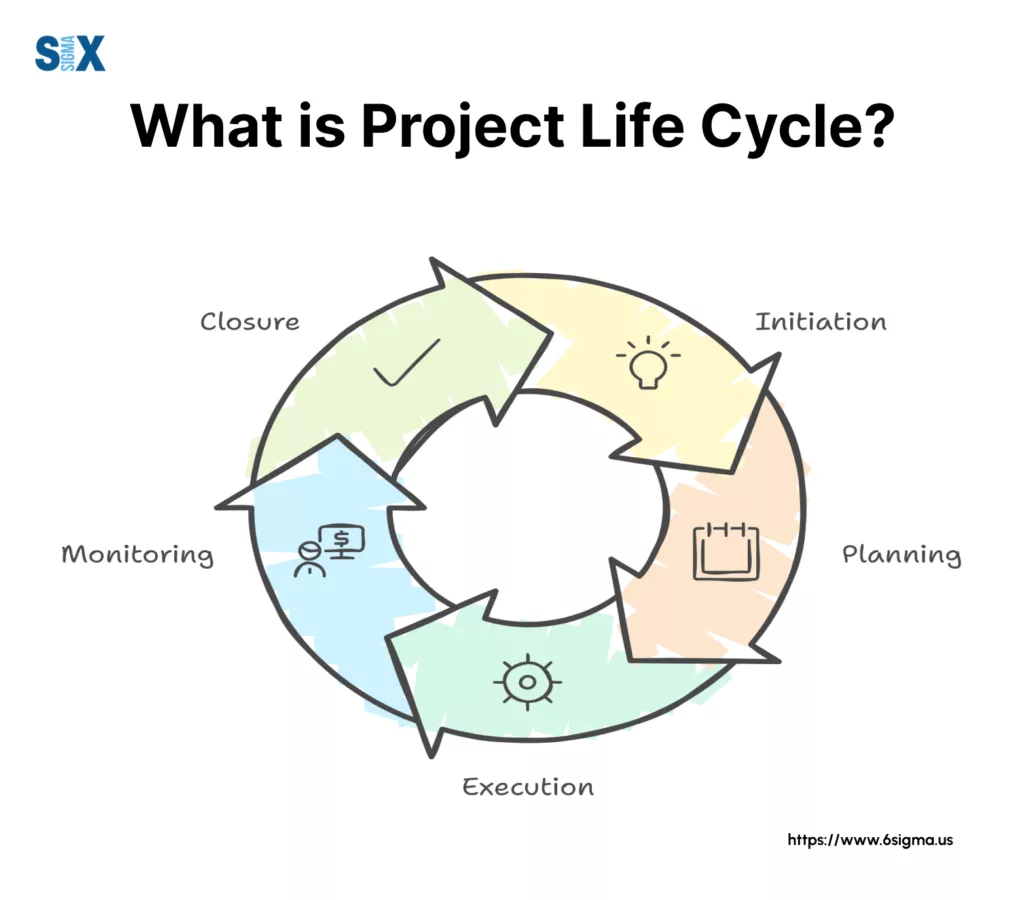
A project life cycle is a set sequence of phases that every project goes through. The terminology used across industries might differ, but the core concept holds consistent, irrespective of project types.
Think of it as the DNA of project management – it provides the basic structure that determines how your project will develop and mature.
When I define a project life cycle to my workshop participants, I often use this simple analogy: just as a butterfly goes through distinct stages of metamorphosis, every project evolves through specific phases, each with its characteristics and challenges.
The Importance of Project Life Cycle Management
What makes this framework so powerful?
The project life cycle provides a structured approach that’s both flexible and robust. It’s like having a GPS for your project – it shows you where you are, where you’re going, and the best route to get there!
Organizations that excel at project life cycle management consistently achieve:
- Better resource allocation and utilization
- More accurate timeline predictions
- Clearer stakeholder communication
- Higher success rates in project delivery
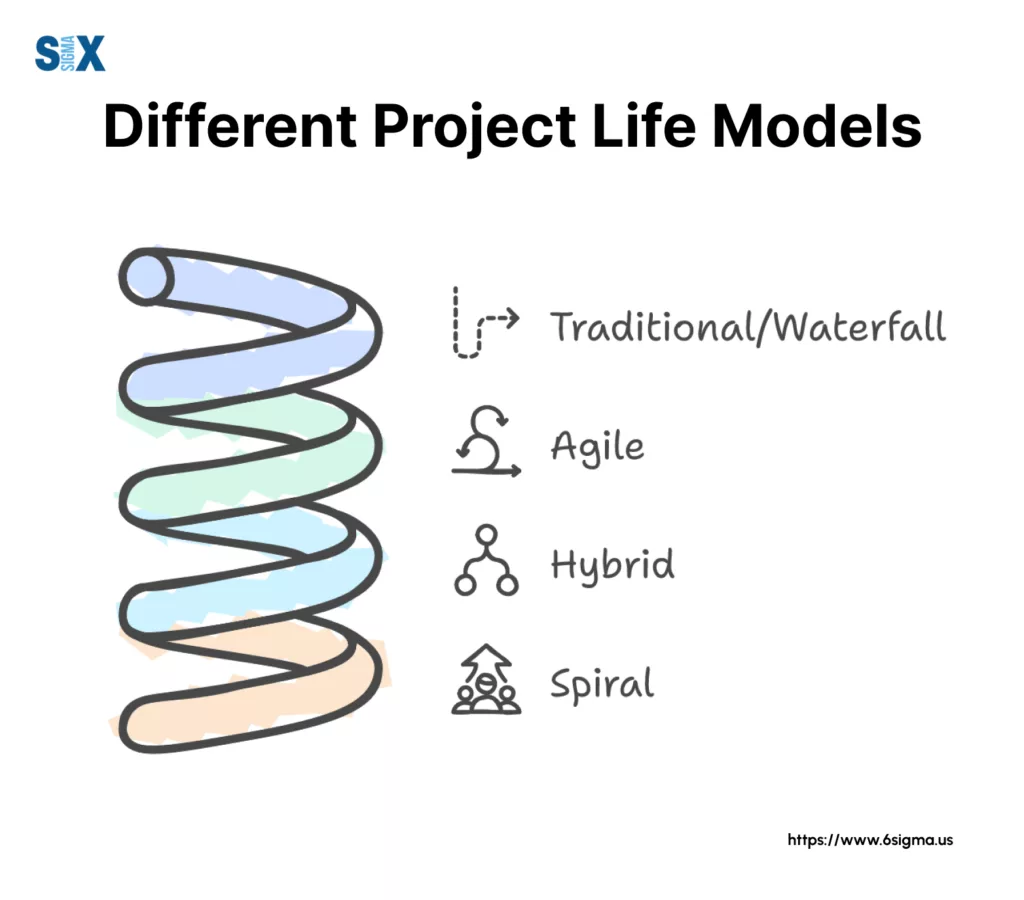
Different Models of Project Life Cycle
Various project life cycle models, each suited to different project types and organizational needs:
- Traditional/Waterfall: Sequential phases with clear handoffs
- Agile: Iterative cycles with continuous feedback
- Hybrid: Combining elements of both approaches
- Spiral: Risk-driven approach common in software development
The Life Cycle Path of a Project
The typical project life cycle path follows a predictable pattern, though the specific details may vary. Each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a comprehensive framework for project success.
Visualizing the project life cycle as a continuous flow rather than discrete steps helps teams understand the interconnected nature of project phases. This understanding is crucial for maintaining momentum and ensuring smooth transitions between phases.
The 5 Phases of the Project Life Cycle: A Master Black Belt’s Guide
Understanding the five phases of the project life cycle is crucial for project success. Let’s walk you through each phase.
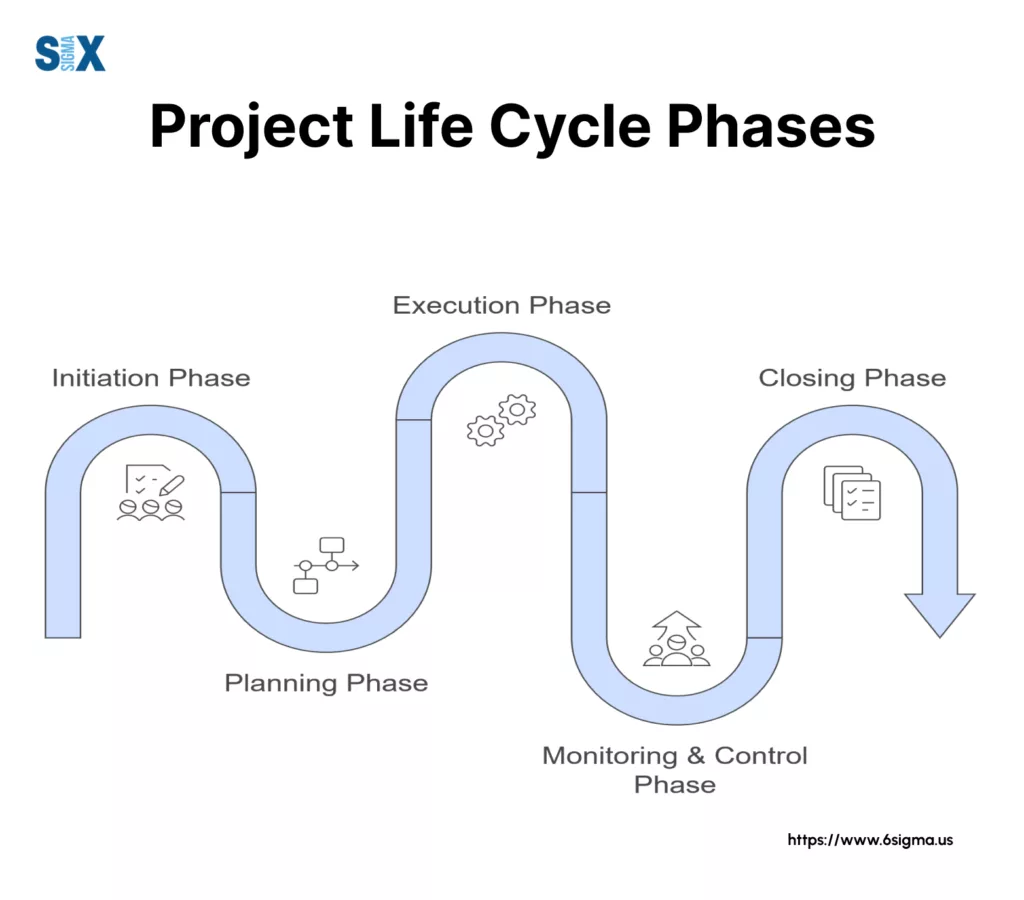
1. Initiation Phase
The initiation phase is where your project takes its first breath. This phase is critical for setting the right foundation. Key activities include:
- Developing the project charter
- Identifying key stakeholders
- Conducting feasibility studies
- Establishing preliminary scope
- Defining success criteria
Master the First Step of Project Success
Our Define Phase and Project Selection course will teach you proven methods to identify impactful projects, create robust project charters, and set your initiatives up for success from day one.
2. Planning Phase
The planning phase is where your project takes shape. Essential elements include:
- Developing the project management plan
- Creating detailed schedules
- Establishing budget parameters
- Defining resource requirements
- Risk assessment and mitigation planning
- Setting quality standards
3. Execution Phase
This is where the rubber meets the road in the project life cycle. Successful execution requires:
- Team mobilization and coordination
- Resource allocation and management
- Implementation of planned activities
- Quality control measures
- Stakeholder communication
- Change management
4. Monitoring and Controlling Phase
This phase runs parallel to execution and is where statistical analysis becomes particularly valuable. Key aspects include:
- Performance tracking
- Progress reporting
- Risk monitoring
- Quality assurance
- Scope management
- Budget control
5. Closing Phase
The often-overlooked final phase of the project life cycle is crucial for organizational learning. Essential activities include:
- Deliverable verification
- Documentation completion
- Resource release
- Stakeholder sign-off
- Lessons learned documentation
- Project closure report
Throughout these stages of the project life cycle, it’s essential to maintain flexibility while following the structured approach. In my experience, the most successful projects are those that adapt these phases to their specific context while maintaining the core principles of each stage.
Remember: The phases of the project life cycle aren’t just sequential steps – they’re interconnected elements that often overlap and interact. Understanding these relationships is key to successful project management.
Best Practices for Each Phase of the Project Life Cycle: Insights from the Field
Here is a set of best practices for each phase of the project life cycle.
Initiation Best Practices
- Conduct thorough stakeholder analysis before project kickoff
- Use data-driven feasibility studies (something I always emphasize in my Six Sigma workshops)
- Create a detailed business case with clear ROI projections
- Establish SMART objectives aligned with organizational goals
Pro Tip: “I always insist on having a project charter template that includes success criteria metrics. This has saved countless projects from scope creep.”s
Planning Best Practices
- Develop detailed work breakdown structures (WBS)
- Create risk registers with mitigation strategies
- Use statistical tools for accurate estimating
- Establish clear communication protocols
- Define quality metrics and acceptance criteria
Execution Best Practices
Through my work in process improvement, I’ve identified these key execution practices:
- Implement daily stand-up meetings for team alignment
- Use visual management boards
- Maintain detailed activity logs
- Follow established change control procedures
- Regular stakeholder updates
Monitoring and Controlling Best Practices
Drawing from my statistical background, I recommend:
- Use statistical process control charts for performance tracking
- Implement earned value management systems
- Conduct regular risk reassessments
- Maintain updated issue logs
- Hold periodic review meetings with key stakeholders
Closing Best Practices
- Document lessons learned systematically
- Conduct formal project reviews
- Archive all project documentation
- Celebrate successes and acknowledge team contributions
- Create actionable recommendations for future projects
The sequence of preparing a project within the project life cycle should follow these practices while maintaining flexibility. Organizations that adapt these best practices to their specific context while maintaining the core principles achieve the best results.
Critical Success Factors:
- Clear documentation at every phase
- Regular stakeholder engagement
- Data-driven decision making
- Proactive risk management
- Continuous improvement mindset
These best practices have been refined through hundreds of projects across different industries and continents. They provide a solid framework for managing each phase of the project life cycle while allowing for the flexibility needed in today’s dynamic business environment.
Common Challenges and Solutions in the Project Life Cycle: Learning from Experience
Let me share some of the most common pitfalls I’ve observed and the solutions that have proven effective across various industries.
1. Scope Creep
This is perhaps the most persistent challenge I’ve encountered in project life cycle management. During a major process improvement project at Dell, we faced significant scope creep that threatened to derail the entire initiative.
Solution Strategy:
- Implement rigid change control procedures
- Document all scope changes formally
- Create clear scope boundaries in the project charter
- Regular scope review meetings
2. Resource Constraints within the Project Life Cycle
In my experience leading international projects, resource management often becomes a critical challenge, particularly in matrix organizations.
Solution Strategy:
- Develop detailed resource forecasting models
- Implement resource leveling techniques
- Create flexible resource pools
- Use statistical analysis for resource optimization
Pro Tip: Always build in a 15-20% resource buffer for critical path activities. This practice has saved countless projects I’ve overseen.
3. Communication Breakdowns
Having worked with diverse teams across multiple continents, I’ve learned that communication issues can derail even the most well-planned projects.
Solution Strategy:
- Establish structured communication protocols
- Use visual management tools
- Implement regular status meetings
- Create clear escalation pathways
4. Risk Management Issues in Project Life Cycle
My statistical background has taught me that effective risk management is often the difference between project success and failure.
Solution Strategy:
- Develop comprehensive risk registers
- Implement proactive risk monitoring
- Use quantitative risk analysis methods
- Regular risk review sessions
5. Stakeholder Conflicts within the Project Life Cycle
Through my experience with various organizations, I’ve found that stakeholder management is often underestimated in project life cycle development.
Solution Strategy:
- Create detailed stakeholder analysis matrices
- Develop targeted communication plans
- Regular stakeholder engagement sessions
- Clear decision-making hierarchies
Pro Tip: I always recommend creating a stakeholder engagement calendar at the project outset. This practice has significantly reduced conflicts in projects I’ve managed.
Key Takeaways
- Prevention is Better Than Cure
In my workshops, I emphasize that identifying potential challenges early in the project life cycle is crucial. It’s much easier to prevent issues than to fix them later. - Data-Driven Decision Making
Use metrics and statistical analysis to support your decisions. This approach has helped me resolve countless project challenges objectively. - Flexible Response Strategies
Having flexible response strategies is crucial for addressing unexpected challenges.
Adapting the Project Life Cycle for Modern Challenges: Embracing Change
Digital transformation has fundamentally altered each project’s life cycle phase. I’ve observed several key changes:
- Automation and AI Integration
- Automated progress tracking
- AI-powered risk prediction
- Machine learning for resource optimization
- Real-time performance analytics
- Digital Collaboration Tools
- Cloud-based project management platforms
- Virtual reality for design reviews
- Digital twin technology
- Integrated communication systems
Adapting for Remote/Distributed Teams
I’ve developed effective strategies for managing distributed teams:
- Communication Protocols
- Structured virtual meetings
- Asynchronous communication guidelines
- Digital documentation standards
- Time zone management strategies
- Team Engagement
- Virtual team building activities
- Digital collaboration spaces
- Cross-cultural communication training
- Remote work best practices
Pro Tip: During a global project, we implemented a ‘follow-the-sun’ workflow that increased productivity by 30%.
Integrating Agile Methodologies within a Project Life Cycle
The traditional project life cycle is evolving to incorporate agile principles. Based on my experience implementing hybrid approaches:
- Hybrid Framework Development
- Combining waterfall and agile elements
- Sprint-based delivery within traditional phases
- Flexible milestone planning
- Adaptive scope management
- Implementation Strategies
- Incremental adoption approach
- Team capability assessment
- Customized training programs
- Performance monitoring systems
Sustainability Considerations
Modern project life cycles must address sustainability:
- Environmental Impact
- Green project management practices
- Sustainable resource allocation
- Carbon footprint monitoring
- Waste reduction strategies
- Long-term Viability
- Sustainable technology choices
- Future-proof design considerations
- Circular economy principles
- Social responsibility integration
Key Adaptation Strategies for Project Life Cycle
- Digital-First Mindset
I always emphasize to my clients that digital transformation isn’t just about tools – it’s about fundamentally rethinking how we approach each project life cycle phase. - Flexibility in Implementation
Successful adaptation requires balancing structure with flexibility. - Continuous Learning
The project life cycle must now include continuous learning and adaptation as core components.
Case Studies: Project Life Cycle Examples
Project life cycle can adapt to different contexts. Let’s look at some case studies to demonstrate the versatility and importance of proper project life cycle management.
Case Study 1: Enterprise-Wide IT System Implementation
Project Overview:
During my work with a technology company, we planned to implement a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system across multiple global locations.
The Five Stages of Project Life Cycle Implementation:
- Initiation:
- Conducted stakeholder analysis across 12 countries
- Developed a comprehensive business case
- Created detailed project charter
- Established success metrics
- Planning:
- Developed phased implementation strategy
- Created risk mitigation plans
- Established change management protocols
- Designed training programs
- Execution:
- Implemented pilot program in two locations
- Rolled out training to 5,000+ users
- Managed vendor relationships
- Coordinated technical teams
- Monitoring:
- Tracked KPIs through a custom dashboard
- Conducted weekly progress reviews
- Managed scope changes
- Monitored budget variance
- Closing:
- Documented lessons learned
- Transitioned to the operations team
- Celebrated success milestones
- Created maintenance protocols
Results: The project was completed 2 months ahead of schedule with 98% user adoption rate.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Facility Construction Project
While working with an industry, worker safety, and consumer goods giant, we oversaw a major construction project that demonstrated the importance of adapting the project life cycle to physical construction requirements.
Key Challenges:
- Multiple contractor coordination
- Environmental compliance
- Safety regulations
- Supply chain management
Implementation Strategy:
- Used hybrid waterfall-agile approach
- Implemented daily stand-up meetings
- Created a visual management system
- Established milestone-based reporting
Results: Achieved zero safety incidents and completed within 3% of the original budget.
Case Study 3: Agile Product Development at a Software Company
During my consultation with an IT company, we implemented an agile product development life cycle for a new software solution.
Innovative Approaches:
- Two-week sprint cycles
- Daily scrum meetings
- Continuous integration/deployment
- User feedback integration
Key Success Factors:
- Flexible Planning:
- Rolling wave planning approach
- Regular backlog grooming
- Stakeholder feedback loops
- Team Structure:
- Cross-functional teams
- Dedicated product owner
- Scrum master rotation
Results: Reduced time-to-market by 40% while improving customer satisfaction scores by 35%.
Pro Tip: The success of any project life cycle implementation depends heavily on team buy-in and cultural alignment.
Common Success Patterns Across Cases of Project Life Cycle
- Clear Communication:
In all three cases, establishing clear communication channels was crucial for success. - Adaptable Framework:
The project life cycle framework needed to be adapted while maintaining core principles. - Stakeholder Engagement:
Regular stakeholder involvement throughout all five stages of the project life cycle proved essential. - Metrics-Driven Approach:
Using data-driven decision-making helped maintain project focus and demonstrate value.
These case studies demonstrate how the project life cycle can be effectively adapted to different contexts while maintaining its core principles. The key is understanding how to apply the framework appropriately for your specific situation.
“While each project is unique, the fundamental principles of the project life cycle remain consistent. It’s how you apply them that makes the difference”.
Next Steps
Understanding and effectively managing the project life cycle is fundamental to project success. By mastering these principles, you’re not just learning a process; you’re acquiring a powerful toolkit for achieving consistent project success.
Your Next Steps:
- Review your current project management practices
- Implement the tools and techniques we’ve discussed
- Adapt the framework to your specific context
- Monitor and measure your improvements
“Success in project management isn’t about perfection – it’s about consistent improvement and adaptation.”
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







