Monitoring and Controlling in Project Management: A Definitive Guide
Project management success hinges on the ability to track progress and make timely adjustments.
Monitoring and controlling serves as the backbone of project execution, enabling project managers to maintain oversight and ensure deliverables meet stakeholder expectations.
This critical phase runs parallel to project execution, forming a continuous feedback loop that helps teams stay aligned with project objectives.
Understanding methodologies like six sigma can provide a powerful framework for process improvement within this phase.
While execution focuses on completing tasks, monitoring and controlling ensures these tasks contribute effectively to project goals.
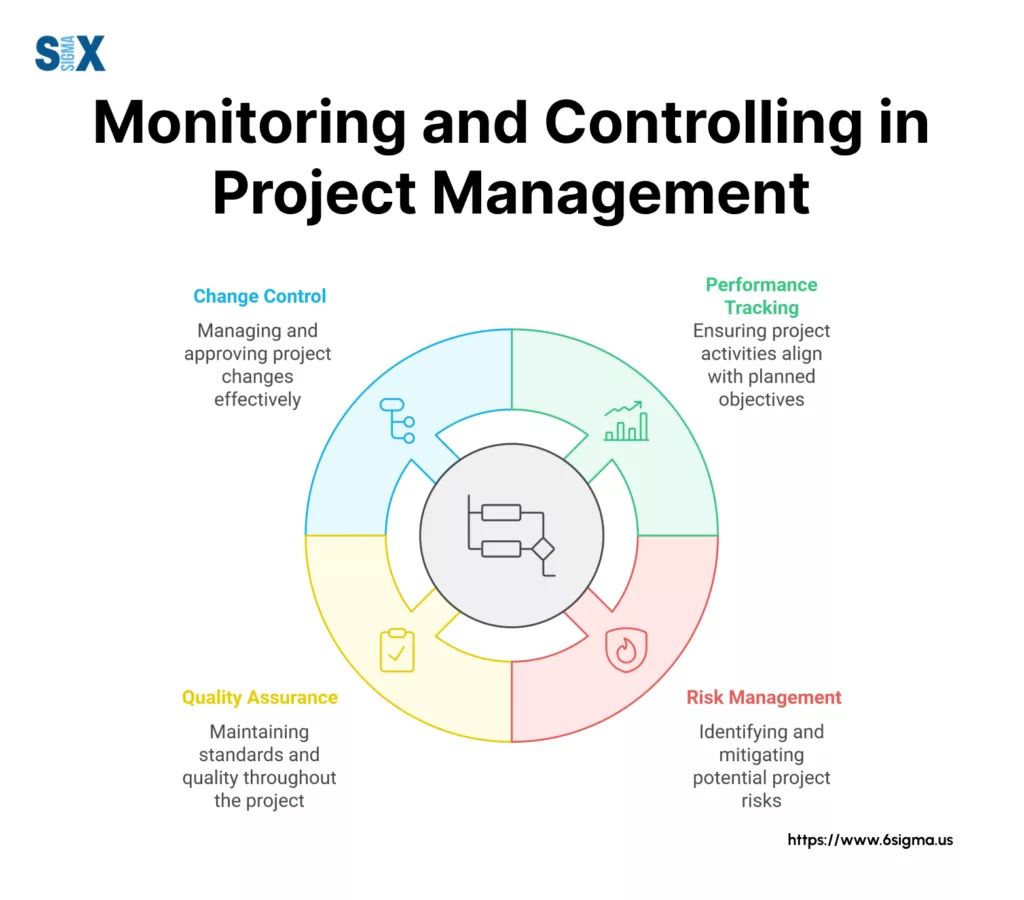
Key Highlights
- Project Performance Tracking Methods
- Baseline Establishment Guidelines
- Real-time Monitoring Techniques
- Risk Management Strategies
- Control Implementation Steps
- Data-driven Decision Making Process
What Is Monitoring and Controlling in Project Management?
Monitoring and controlling represents the fourth phase of project management, serving as the oversight mechanism that keeps projects on track.
This phase ensures projects meet their intended goals through systematic observation and adjustment of project activities.
Core Elements of Project Monitoring
Project monitoring focuses on measuring and tracking project performance against established plans.
Project managers collect data on task completion, resource usage, and budget expenditure to maintain visibility into project progress.
Through regular status meetings and performance reports, teams can identify potential issues before they impact project outcomes.
The monitoring process includes tracking key metrics such as:
- Schedule performance indicators
- Cost variance analysis
- Quality metrics
- Resource utilization rates
- Risk assessment data
Master Project Monitoring Fundamentals with Define Phase and Project Selection Course
The Control Function in Projects
Project controlling moves beyond observation to active intervention. When monitoring reveals deviations from the plan, controlling activities help bring the project back on course.
This includes implementing corrective actions, adjusting resource allocations, and modifying project parameters as needed.
Integration of Monitoring and Controlling Within Project Lifecycle
Monitoring and controlling operates alongside project execution, creating a dynamic feedback loop. While teams work on deliverables, project managers maintain oversight through:
- Regular performance reviews
- Status updates and reporting
- Risk assessment meetings
- Quality control checks
- Change management procedures
Distinguishing Monitoring From Controlling
Though interconnected, monitoring and controlling serve distinct purposes. Monitoring acts as the project’s radar system, detecting variations from planned performance.
Controlling represents the steering mechanism, implementing changes to maintain the correct course.
For example, monitoring might reveal that a software development project is falling behind schedule.
The controlling function would then determine appropriate actions, such as adding resources or adjusting the project timeline.
Role in Project Success
Effective monitoring and controlling significantly influences project outcomes.
Studies show that projects with robust monitoring and controlling processes are 2.5 times more likely to finish on time and within budget. This phase helps project managers:
- Maintain alignment with project objectives
- Ensure efficient resource utilization
- Control costs and prevent overruns
- Manage stakeholder expectations
- Address risks proactively
The monitoring and controlling phase requires continuous attention throughout the project lifecycle.
By maintaining vigilant oversight and implementing timely corrections, project managers can guide their projects toward successful completion.
The Importance of Monitoring and Controlling
Project success rates increase by 65% when organizations implement effective monitoring and controlling practices.
This significant improvement demonstrates why this phase stands as a crucial element in project management methodologies like Six Sigma.
Keeping Projects On The Intended Path
Monitoring and controlling serves as an early warning system for project deviations.
Project managers who maintain consistent oversight can spot variations from planned parameters before they escalate into major issues.
Regular tracking of key performance indicators enables teams to maintain momentum and meet project milestones on schedule.
Through systematic monitoring, project teams can:
- Track actual progress against planned timelines
- Measure resource utilization efficiency
- Compare actual costs to budgeted amounts
- Evaluate quality metrics against standards
Risk Management and Issue Prevention
Early detection of potential problems through a root cause analysis remains one of the most valuable benefits of project monitoring and controlling.
Project managers who implement robust monitoring systems can identify risks before they materialize into issues.
This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of schedule delays, cost overruns, and quality compromises.
Data-Driven Decision Making with Monitoring and Controlling
Project monitoring generates valuable data that supports informed decision-making.
When project managers have access to real-time performance metrics, they can:
- Make evidence-based adjustments to project plans
- Allocate resources more effectively
- Justify changes to stakeholders
- Predict future project outcomes
Building Stakeholder Trust
Regular monitoring and controlling activities help maintain stakeholder confidence.
When project managers can demonstrate clear oversight and control of project activities, stakeholders feel more assured about project investments and outcomes.
Stakeholder alignment can be further strengthened through our Six Sigma certification programs, which emphasize also on data-driven communication.
Key stakeholder benefits include:
- Regular status updates
- Clear visibility into project progress
- Confidence in project management capability
- Early awareness of potential issues
Financial Control and Resource Optimization with Monitoring and Controlling
Effective monitoring and controlling, combined with the fundamentals of Lean, helps organizations optimize resource usage and maintain budget control.
Project managers can track expenditure patterns, identify cost-saving opportunities, and ensure resources deliver maximum value to the project.
Statistics show that projects with structured monitoring systems experience:
- 25% reduction in budget overruns
- 30% improvement in resource utilization
- 40% decrease in timeline extensions
- 50% better stakeholder satisfaction rates
Quality Assurance and Standards Compliance
Monitoring and controlling ensures deliverables meet quality standards throughout the project lifecycle.
Regular quality checks and performance monitoring help maintain consistency and reduce the need for costly rework or corrections later in the project.
The implementation of monitoring and controlling practices represents an investment in project success.
Organizations that prioritize these activities see measurable improvements in project outcomes, stakeholder satisfaction, and resource efficiency.
The Monitoring and Controlling Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Successful project monitoring and controlling requires a structured approach that enables project managers to track progress and make timely adjustments.
This systematic process helps teams maintain project health and achieve desired outcomes.
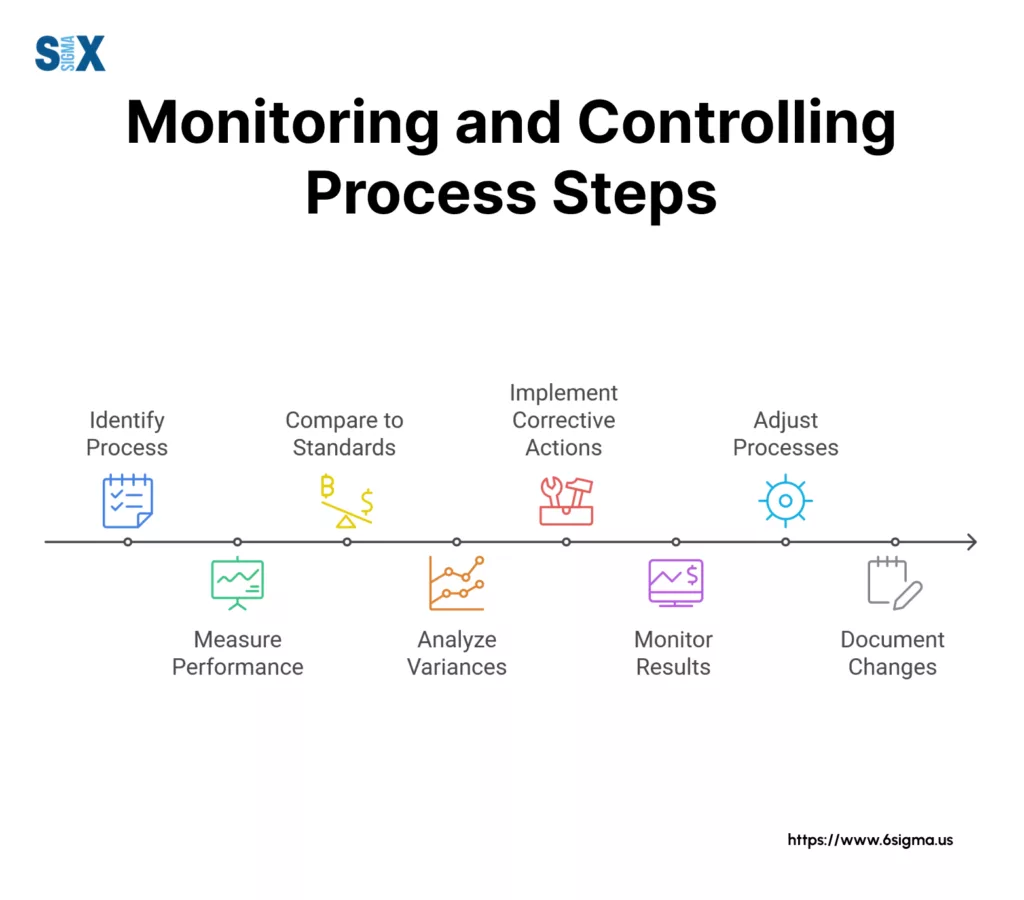
Establishing Project Baselines
Project baselines form the foundation for effective monitoring and controlling.
These benchmarks include schedule, cost, and scope parameters against which actual performance will be measured. Project managers must document:
- Schedule milestones and deadlines
- Budget allocations and cost estimates
- Quality standards and acceptance criteria
- Resource requirements and availability
- Scope boundaries and deliverables
Performance Data Collection with Monitoring and Controlling
Regular data collection enables project managers to maintain visibility into project progress. This stage involves gathering information through:
- Status meetings with team members
- Time and expense tracking systems
- Quality control inspections
- Resource utilization reports
- Risk assessment updates
The frequency of data collection should align with project complexity and stakeholder reporting requirements.
Variance Analysis and Assessment
Once data is collected, project managers analyze variances between planned and actual performance.
This analysis reveals whether the project remains on track or requires intervention, i.e. needing to address the root causes. Key areas for variance analysis include:
- Schedule performance indices
- Cost variance calculations
- Quality metrics evaluation
- Resource utilization rates
- Risk impact assessments
Progress Reporting and Communication
Clear communication of project status keeps stakeholders informed and engaged.
Project managers should create regular reports that highlight:
- Current project status
- Identified variances
- Potential risks and issues
- Recommended actions
- Updated forecasts
These reports should be tailored to different stakeholder groups, ensuring relevant information reaches the right audience.
Implementing Corrective Actions with Monitoring and Controlling
When variances exceed acceptable thresholds, project managers must implement corrective actions.
This final stage involves:
- Developing action plans
- Allocating necessary resources
- Updating project documents
- Communicating changes to stakeholders
- Monitoring the effectiveness of interventions
The success of corrective actions often depends on their timeliness and appropriateness to the situation.
Continuous Process Improvement
The monitoring and controlling process should evolve based on project needs and organizational learning.
Project managers should regularly evaluate the effectiveness of their monitoring approaches and adjust as needed.
Successful organizations typically see:
- 20% faster issue resolution
- 35% improvement in stakeholder satisfaction
- 40% reduction in project delays
- 50% better resource utilization
This systematic approach to monitoring and controlling helps project managers maintain oversight while providing clear pathways for intervention when needed.
By following these structured steps, teams can better ensure project success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Monitoring and Controlling
Modern project management relies on various tools and techniques to maintain effective monitoring and controlling processes. These tools help project managers track progress, identify issues, and make data-driven decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Popular tools used in project monitoring and controlling processes
Asana
Jira
Basecamp
Trello
Earned Value Management (EVM)
EVM stands as a powerful technique for measuring project performance and progress, and is a core component of Six Sigma methodologies. This method combines scope, schedule, and cost metrics to provide clear insights into project health. Project managers use EVM to:
- Calculate schedule performance index (SPI)
- Determine cost performance index (CPI)
- Forecast project completion dates
- Estimate final project costs
- Track variance trends
Organizations implementing EVM report 30% more accurate project forecasts and 25% better budget control.
Critical Path Method (CPM)
CPM helps project managers identify and monitor crucial project activities. This technique maps dependencies between tasks and determines the longest path through the project schedule. Key benefits of CPM include:
- Clear identification of critical activities
- Better schedule control
- Improved resource allocation
- Early warning of potential delays
- Enhanced timeline management
Project Management Software Solutions
Digital tools streamline monitoring and controlling activities while providing real-time insights into project performance.
Modern project management software offers:
- Automated progress tracking
- Resource management capabilities
- Budget monitoring features
- Risk management modules
- Customizable dashboards
Visual Management Tools for Monitoring and Controlling
Gantt charts and other visual tools provide clear representations of project progress and timeline management.
These tools help teams:
- Visualize project schedules
- Track milestone completion
- Monitor task dependencies
- Identify schedule conflicts
- Communicate progress to stakeholders
Performance Measurement Tools
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics tracking tools help quantify project progress.
Essential measurements include:
- Schedule variance
- Cost performance
- Quality metrics
- Resource utilization
- Risk indicators
Change Control Systems for Monitoring and Controlling
Structured change management tools help teams track and control modifications to project scope, schedule, or budget.
These systems typically include:
- Change request forms
- Impact assessment tools
- Approval workflows
- Change logs
- Implementation tracking
Reporting and Dashboard Tools
Regular reporting tools provide stakeholders with visibility into project status and performance.
Effective reporting systems should deliver:
- Status updates
- Performance metrics
- Risk assessments
- Resource allocation views
- Trend analysis
Project managers who utilize these tools effectively report:
- 40% improved project visibility
- 35% better stakeholder communication
- 45% faster issue resolution
- 50% more accurate forecasting
The selection of appropriate monitoring and controlling tools depends on project size, complexity, and organizational requirements. Integration between different tools often provides the most effective solution for project oversight.
Common Challenges in Monitoring and Controlling (and How to Overcome Them)
Project monitoring and controlling faces several recurring challenges that can impact project success.
Understanding these obstacles and implementing effective solutions helps project managers maintain better control over their projects.

Managing Scope Creep
Scope creep remains one of the most prevalent challenges in project monitoring and controlling.
Projects often expand beyond their original boundaries due to changing requirements or stakeholder requests. This expansion can lead to timeline delays and budget overruns.
To combat scope creep, project managers should implement strict change control processes.
These processes must include clear documentation requirements, impact assessments, and stakeholder approval workflows. Regular scope reviews and baseline comparisons help identify potential deviations early.
Addressing Inaccurate Reporting
Inaccurate or delayed reporting creates significant obstacles in project monitoring. When team members provide incomplete or incorrect information, project managers struggle to make informed decisions.
This challenge often stems from complex reporting systems or unclear requirements.
The solution lies in standardizing reporting processes and implementing user-friendly tools.
Automated data collection systems reduce human error, while clear reporting templates ensure consistency.
Regular training sessions help team members understand the importance of accurate reporting and proper documentation methods.
Overcoming Resistance to Change within Monitoring and Controlling
Team members often resist new monitoring and controlling processes, viewing them as bureaucratic overhead rather than valuable project tools.
This resistance can lead to poor adoption of monitoring procedures and incomplete project data.
Successful project managers address this challenge through clear communication of benefits and stakeholder engagement.
Demonstrating how monitoring processes improve project outcomes and reduce work redundancy helps gain team buy-in. Including team members in the process development phase increases ownership and adoption.
Dealing With Resource Constraints
Limited resources often hamper effective monitoring and controlling efforts. Project managers must balance the need for thorough oversight with available time and personnel constraints.
The solution involves prioritizing critical monitoring activities and leveraging automation tools. Risk-based monitoring approaches help focus resources on high-priority areas.
Project management software can automate routine tasks, freeing up time for more strategic monitoring activities.
Maintaining Data Quality within Monitoring and Controlling
Poor data quality undermines the effectiveness of monitoring and controlling processes. Inconsistent or outdated information leads to faulty decision-making and reduced stakeholder confidence.
Implementing data validation procedures and regular audits helps maintain data integrity.
Establishing clear data entry standards and providing proper training ensures consistent information quality across the project.
Ensuring Timely Response
Delayed responses to identified issues can compound problems and increase their impact on project outcomes.
Project managers must establish efficient decision-making processes to address challenges promptly.
Creating escalation procedures and defining clear authority levels helps speed up response times.
Regular status meetings and real-time monitoring tools enable faster issue identification and resolution.
Project managers who successfully address these challenges typically see:
- Reduced scope creep by 40%
- Improved reporting accuracy by 35%
- Increased team engagement by 45%
- Better resource utilization by 30%
The key to overcoming these challenges lies in proactive planning, clear communication, and consistent implementation of monitoring and controlling processes.
By addressing these common obstacles head-on, project managers can maintain better project control and achieve higher success rates.
Overcome Project Monitoring Challenges with Lean Six Sigma Organizational Deployment Training
Moving Forward With Effective Project Monitoring and Controlling
The success of modern projects heavily depends on robust monitoring and controlling practices.
Organizations that implement structured oversight processes consistently achieve better project outcomes and maintain stronger stakeholder relationships.
Key Takeaways for Project Success
Project monitoring and controlling serves as the foundation for successful project delivery.
Through systematic tracking and timely interventions, project managers can guide their initiatives toward desired outcomes while minimizing risks and optimizing resource usage via Lean methodologies.
The implementation of proper monitoring tools and techniques enables teams to track progress effectively and respond to changes promptly.
From earned value management to critical path analysis, these tools provide the necessary insights for informed decision-making.
Building on Best Practices
Successful project monitoring requires more than just tools and techniques. It demands a culture of transparency, regular communication, and commitment to continuous improvement.
Organizations must foster an environment where monitoring activities are viewed as valuable contributors to project success rather than administrative burdens.
Statistics show that projects with established monitoring and controlling processes achieve:
- 35% higher success rates
- 40% better budget adherence
- 45% improved stakeholder satisfaction
- 50% faster issue resolution times
Looking Ahead
The field of project monitoring and controlling continues to evolve with technological advancements.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities are enhancing predictive analytics, while automated reporting tools streamline data collection and analysis processes.
Project managers must stay current with these developments while maintaining focus on fundamental monitoring principles.
The balance between traditional oversight methods and innovative technologies will shape the future of project monitoring and controlling.
Final Thoughts
Effective project monitoring and controlling remains essential for delivering successful projects.
By embracing structured oversight processes, leveraging appropriate tools, and maintaining stakeholder engagement, organizations can significantly improve their project outcomes.
The investment in robust monitoring and controlling practices yields substantial returns through improved project performance, reduced risks, and enhanced stakeholder satisfaction.
As project complexity continues to increase, the importance of these practices will only grow stronger.
Successful project monitoring and controlling is not a destination but an ongoing journey of improvement and adaptation.
Organizations that commit to excellence in these areas position themselves for sustained project success.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs







